| Microbe and our body |
When bacteria or a virus enters into our body |
|
|
What will happen to our body?
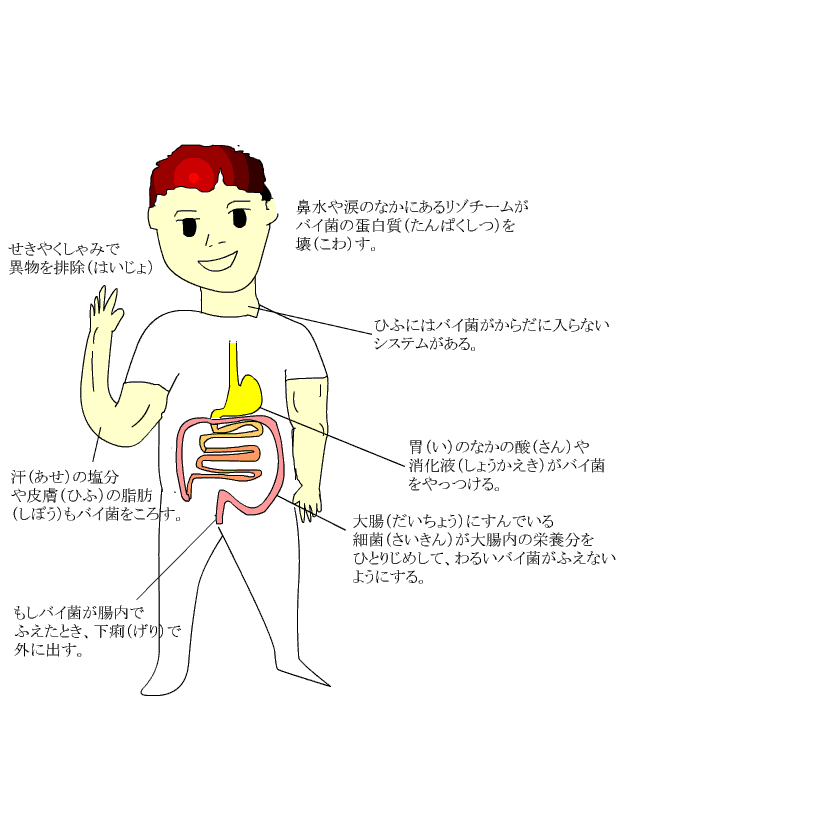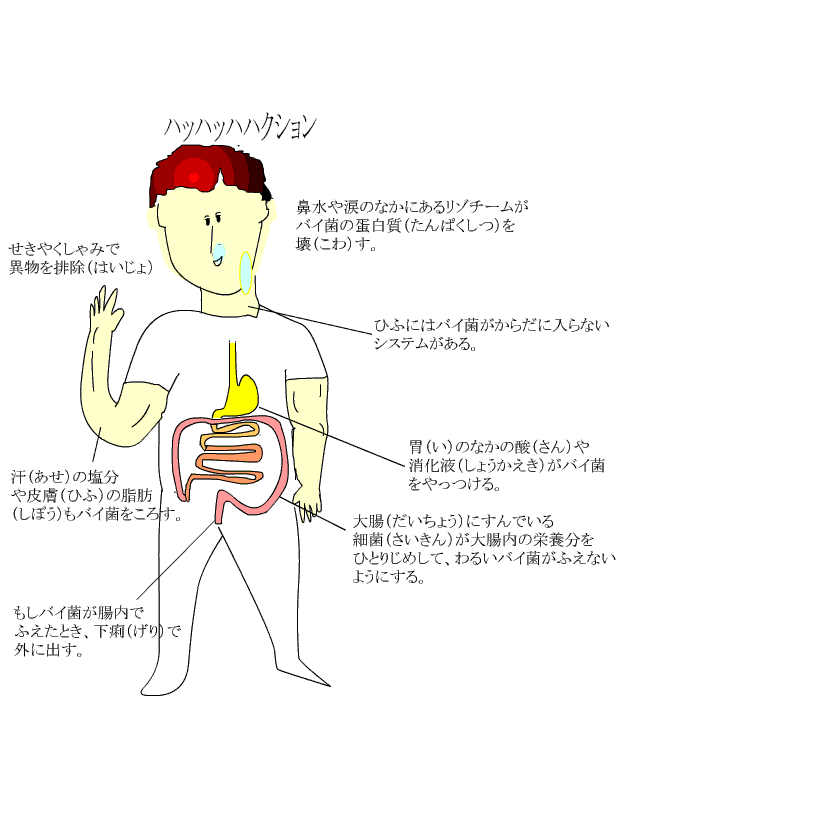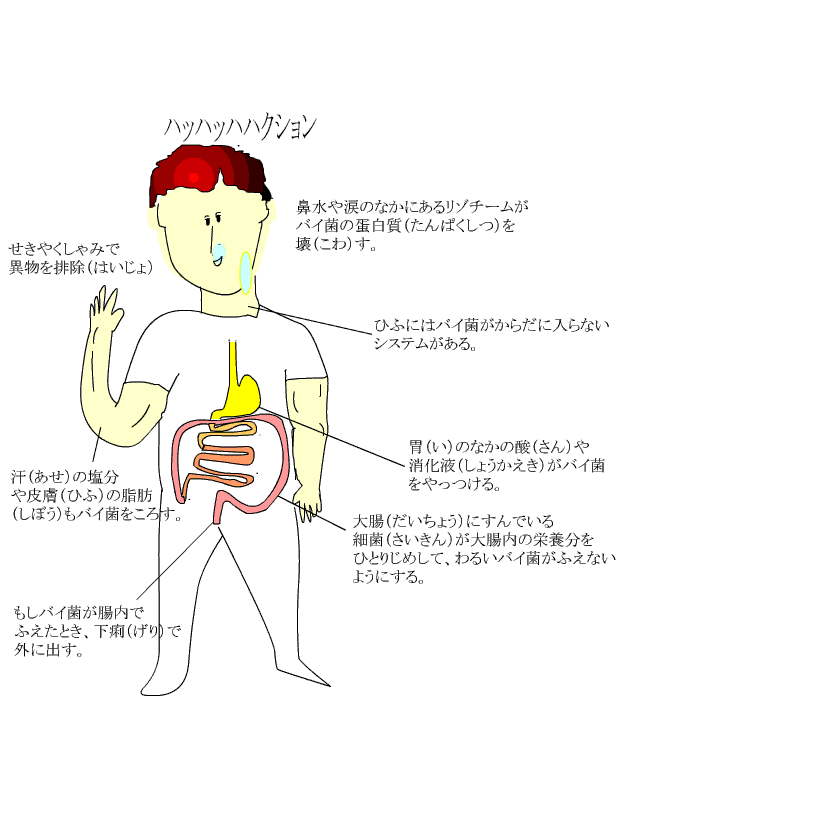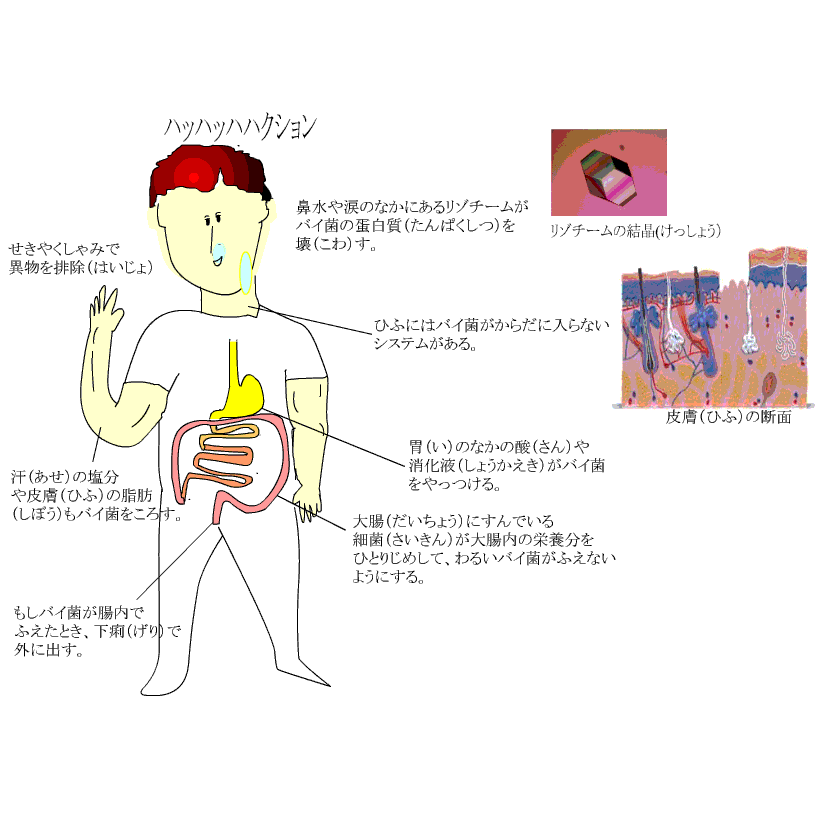
First, our body deals by the method below. In other words, our body removes it physically so that a microbe does not enter to the deep inside of the body. |
|
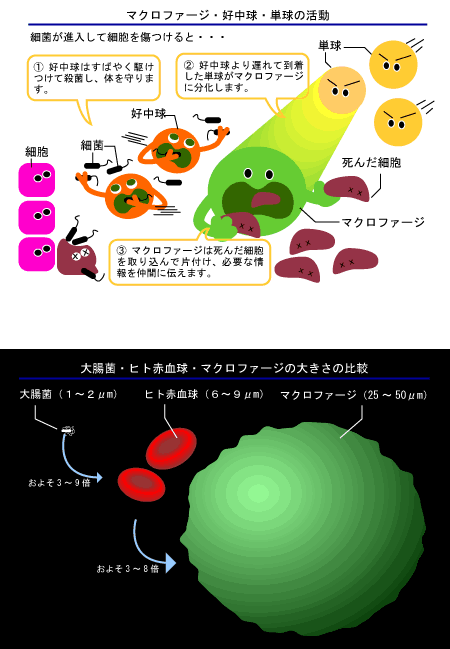
When a microbe invaded to the inside of the body because our condition is bad, a neutrophil in the white blood cell, a macrophage and a natural killer cell protect a body.
It is also a natural immunities. |
| neutrophil |
macrophage |
natural killer cell |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Photo credit - Mr. Tsutomu Itoyama , a laboratory technician of Nagasaki memorial hospital |
A photo is reprinted under the special permission of Foundation for Louis Pasteur Medical Research Center |
|
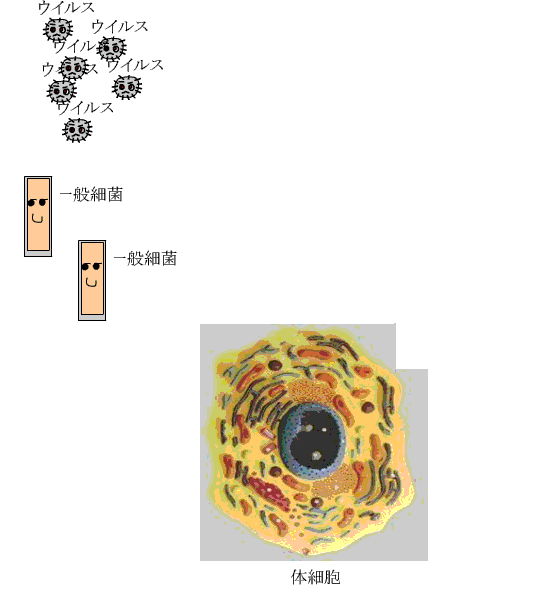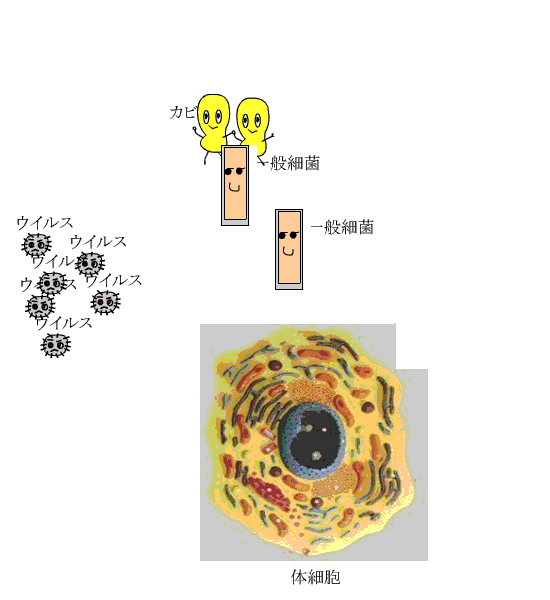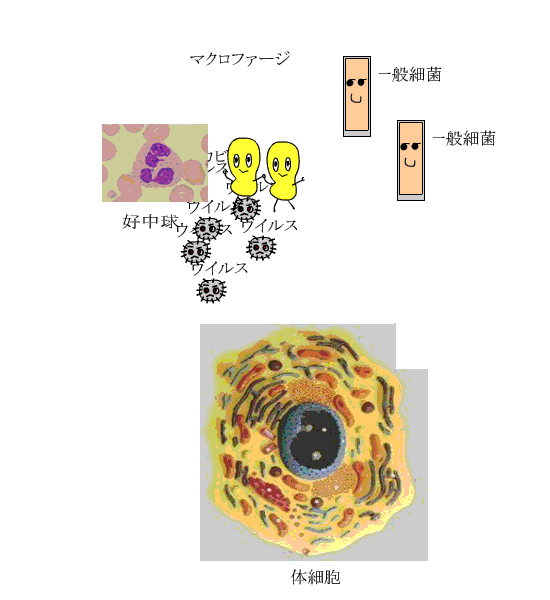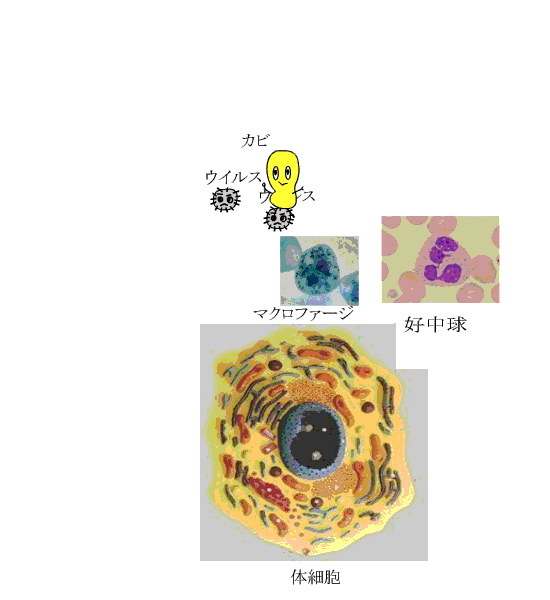
ウイルス:virus、カビ:mold、一般細菌:bacteria、好中球:neutrophils、マクロファージ:macrophage、体細胞:somatic cell |
Except a certain bacterium, many bacteria and mold cannot be alive in our cells. Because
they do not have methods to enter inside.
On the other hand, the viruses can multiply only in a cell and have a method to invade in our cell.
|
|
As for a neutrophil, please refer to “What is blood?” as well.
What move small are bacteria. They disappear from surround. They are eaten by neutrophils, and die. |
 |
There are eaten bacteria in neutrophils. |
|
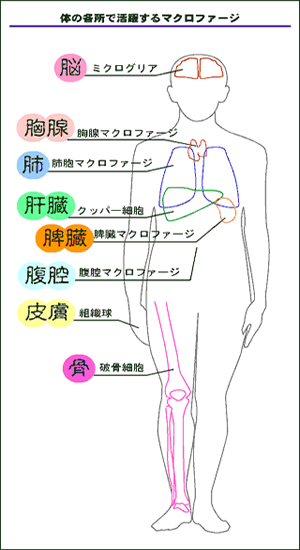
| Macrophage is |
|
| A macrophage appears after a neutrophils, and eats and kills viable bacteria, mold and a virus. |
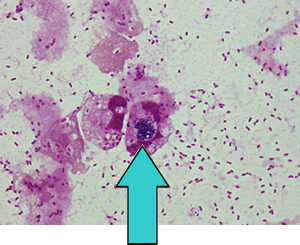
| In viable bacteria, there are strange ones. They have a method to enter a somatic cell and can continue living in it without dying even if eaten by a macrophage unlike other bacteria. |
| Tubercle bacillus as a representative |
Unlike bacteria seen commonly, the tubercle bacillus continues living in a macrophage. In addition, when tuberculosis does not finish being cured, a tubercle bacillus and a tissue around it become calcified, and the tubercle bacillus continues living in them.
Most of Japanese adults 40 years or older are probably infected with a tubercle bacillus in the past. If these people get old, and their immune systems weaken, there is a possibility that they become sick.
Presently, about one third of the whole world population is infected with a tubercle bacillus and seems to be in danger of onset of disease in approximately 10% of it.
In addition, approximately 3 million people die of tuberculosis throughout the world a year. |
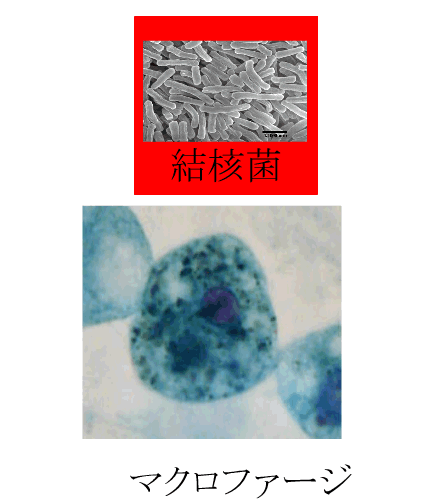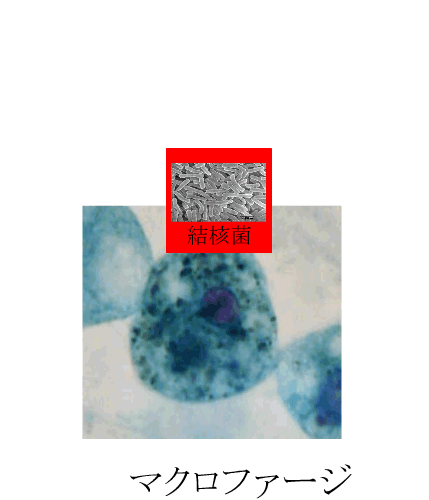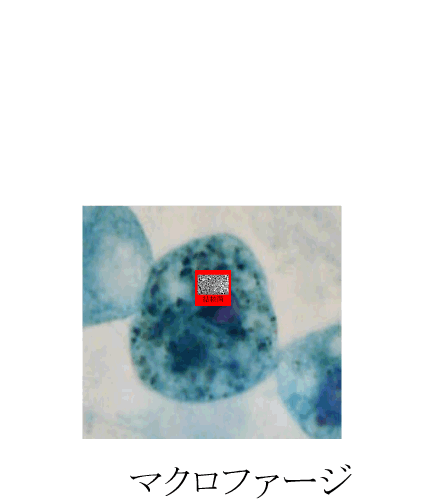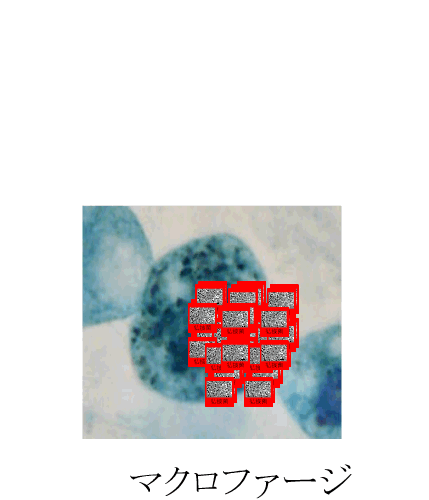
結核菌:tubercule bacillus、マクロファージ:macrophage |
| NK cell |
|
A virus is the microbe which can continue increasing only in a living cell. So are rickettsia, chlamydia, and a mycoplasma.
Basically, since these microbes do not have most metabolism mechanisms, such as energy production and protein synthesis, etc. required for propagation, they cannot but be parasitic in other living cells. |
| The virus which survived without being eaten by a neutrophils or a macrophage enters our somatic cell to live. |
 |
A neutrophils or a macrophage cannot beat the virus which entered in the cell |
|
The cell whose virus is continuing increasing is unnecessary for us. Rather it is necessary to dispose of the cell early because viruses increase.
|
|
It is the appearance of NK cell. |
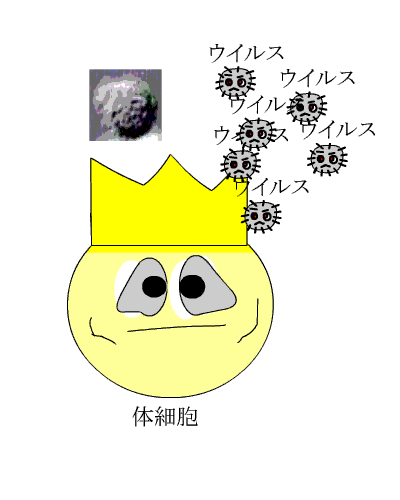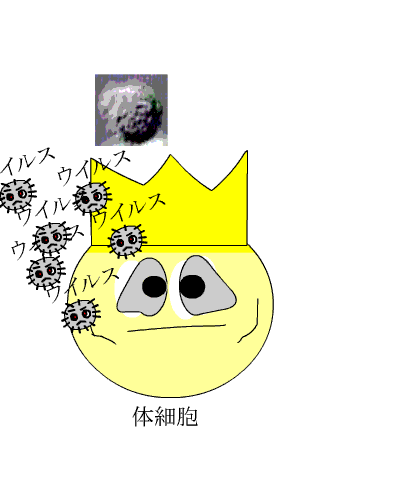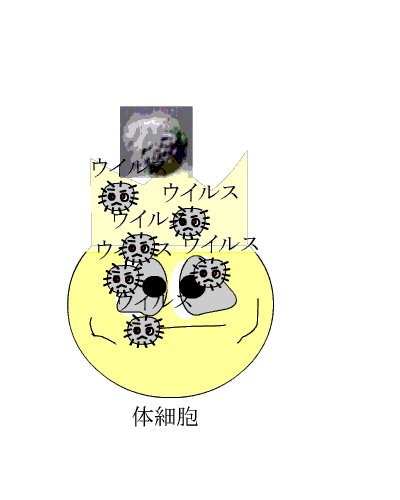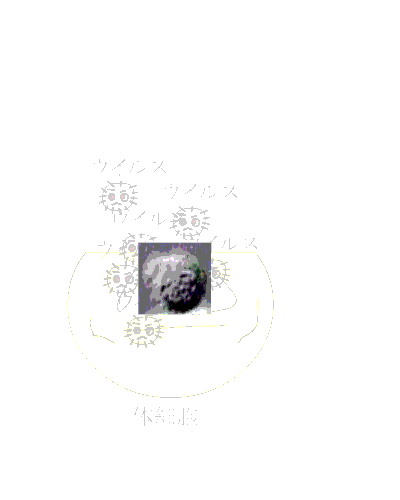
ウイルス:virus、体細胞:somatic cell |
The virus which survived without being attacked by a macrophage and a white blood cell in the outside of a cell enters in a cell.
The cell got into to a virus, the thing which was one's mark called the MHC class 1 molecules we mentioned before (the one shown with a crown in the animation) may transform a little.
A crown is disappearing a little.
The cell which MHC class 1 molecules transformed becomes the cell which cannot perform normal work.
NK cell becomes useless for this role, and processes the cell whose virus is increasing.
This is a natural immunity as well. |
NK cell processes the cancerated cell too other than a cell damaged by a virus. |
|
|
Well, what methods protect ourselves from a microbe except for the natural immunity containing a granulocyte, a macrophage and NK cell? |
|
The answer is the acquired immunity. Next, let’s study about it.
An acquired immunity is literally to acquire the method of eliminating a foreign substance for ourselves.
Particularly, a neutrophil, a macrophage and NK cell work hard for the infection first, and it is all right if a body does not have a big abnormality.
However, various microbes may attack us again. In addition, an infection may be prolonged.
At this time, our body performs the next preparation. |
A dendritic cell, the B cell and T cell and so on which are in a lymphatic tissue play an active parts. |
Dendritic precursor cell (fetal liver derivation) |
B cell cannot be distinguished from T cell to the eye. |
 |
 |
| Lonza Group Ltd. has a copyright of this image and it is placed in the homepage of Sanko Junyaku Co., Ltd (current: EIDIA Co., Ltd.). |
|
http://www.sanko-junyaku.co.jp/product/bio/catalog/nhc/immune_dendritic-pre.html
We have a permission for diversion of the URL |
|
| This cell also eats the microbe of a foreign substance for a human body like a macrophage. However, the power to eat is weaker than macrophage’s one. |
| Then, what does it do? |
| After catching a virus and bacteria, this dendritic cell goes into a lymphatic tissue while breaking down a virus and bacteria and having the leftovers in a cell. |
| In a lymph node, this cell carries out the help with which a B cell and a T-lymph cell build an antibody. A macrophage also carries out this help although it is not so much as a dendritic cell. |
As for the mechanism of the help, please refer to “acquired cell”. |
 |